Motivation is an integral aspect of day-to-day life, aptly called “drive”, motivation is the vehicle to achieving our goals. It impacts how one perceives a certain task as well as their investment in it, and most importantly, their persistence at the same (Filgona et al., 2020). In this blog, we will delve into the science of motivation, exploring strategies that can help leaders inspire their teams and keep them consistently engaged in their work.
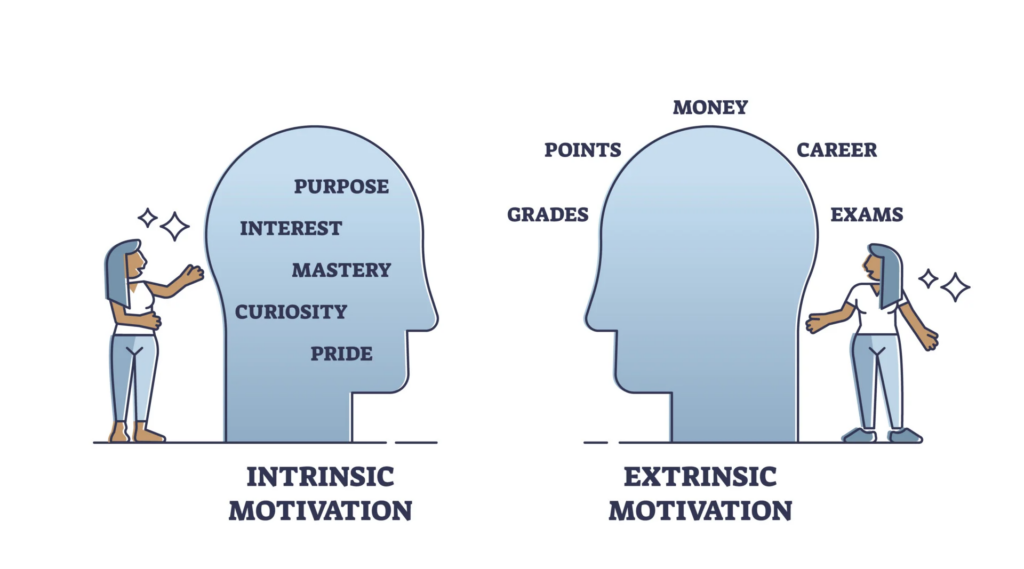
There are broadly two categories of motivation:
- Intrinsic motivation – Intrinsic motivation refers to intangible positive feelings generated internally from participation in a certain activity. For example, children skip and jump because of the internal reward they experience on doing so.
- Extrinsic motivation – Extrinsic reward on the other hand refers to motivation derived from sources which lie outside the person demonstrating the behavior. For example, salary (Legault, 2020).
According to Filgona and colleagues, (2020), “Motivation is the key to success in the teaching-learning process” (pp.16-37). Given the same, it is essential that teachers effectively integrate pedagogical, professional, personal, and social competencies to create a stimulating and engaging environment wherein students excel (Atma et al., 2021). That is, teachers need to use available resources, including presentations, games, and of course their own skills to holistically engage the class in an environment which facilitates learning.
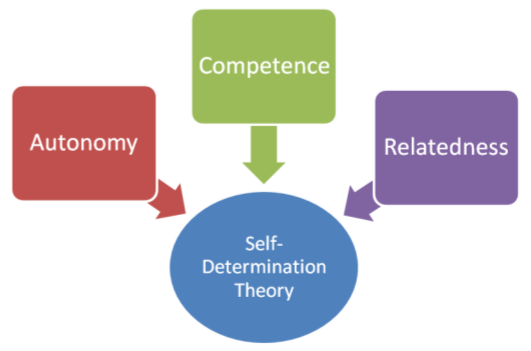
The self-determination theory (SDT) suggests, that when students experience autonomy, competence, and relatedness; that is, they experience a sense of freedom, a sense of proficiency, and are able to feel a connection with the teacher, they are highly motivated to learn (Vermote et al., 2020). Taking the above, and the SDT into consideration, we develop an understanding that while external resources are important for stimulation, internal factors play an equally critical role in the learning process.
While the above-mentioned factors are critical to motivating students to learn, technological developments have created a scenario wherein the importance of relationships is weakened, given the ease of access without human contact. However, while one would expect students to be motivated to use AI-tools to enhance their learning experience, Ali and colleagues’ (2023) study found that students had a neutral attitude to ChatGPT, one of the most commonly used AI-tools.

In summary, motivation is essential for effective learning and can be influenced by both intrinsic and extrinsic factors. Intrinsic motivation stems from personal satisfaction and internal rewards, while extrinsic motivation comes from external incentives like grades or salary. Teachers play a crucial role in fostering motivation by creating an engaging and supportive environment that taps into students’ autonomy, competence, and sense of connection. Despite technological advancements, such as AI tools, which promise to enhance learning, the human element remains vital. Studies, like those by Ali et al. (2023), reveal that students may not always be enthusiastic about these technologies, highlighting the ongoing need for meaningful interpersonal interactions. Balancing technological resources with personal engagement is key to maintaining high levels of motivation and ensuring a successful learning experience.
References
- Ali, J. K. M., Shamsan, M. A. A., Hezam, T. A., & Mohammed, A. A. (2023). Impact of ChatGPT on learning motivation: teachers and students’ voices. Journal of English Studies in Arabia Felix, 2(1), 41-49.
- Atma, B. A., Azahra, F. F., Mustadi, A., & Adina, C. A. (2021). Teaching style, learning motivation, and learning achievement: Do they have significant and positive relationships. Jurnal Prima Edukasia, 9(1), 23-31.
- Filgona, J., Sakiyo, J., Gwany, D. M., & Okoronka, A. U. (2020). Motivation in learning. Asian Journal of Education and social studies, 10(4), 16-37.
- Legault, L. (2020). Intrinsic and extrinsic motivation. Encyclopedia of personality and individual differences, 2416-2419.
- Vermote, B., Aelterman, N., Beyers, W., Aper, L., Buysschaert, F., & Vansteenkiste, M. (2020). The role of teachers’ motivation and mindsets in predicting a (de) motivating teaching style in higher education: A circumplex approach. Motivation and emotion, 44, 270-294.

